Container Apps - Setting storage directory permissions
This blog post will quicky cover how to set storage mount permissions for directories between SMB and NFS on Azure Container Apps.
Overview
Azure Container Apps Storage Mounts support the use of Azure Files - where both SMB and NFS volumes can be used
NOTE: NFS volumes are currently in preview as of writing this blog post on 12/30/2024.
In some cases, you may want to set directory-level Linux permissions on the mount. This post will go over how to do this.
SMB
SMB volumes can be created by following Container Apps - Azure Files volume - SMB
A very important callout - You cannot change permissions for a mount directory with something like chmod at runtime from within a container when using SMB mounts with Azure Files.
You can however utilize the Mount options available when creating a volume, you can pass cifs mount options to change aspects of permissions for the mount (at mount time).
For instance, the default permissions for a Storage resource upon creation is 777 when using Read/write and Read only (although Read only has a read-only filesystem mounted) - but if you wanted to change this, you can pass in the dir_mode and file_mode arguments.
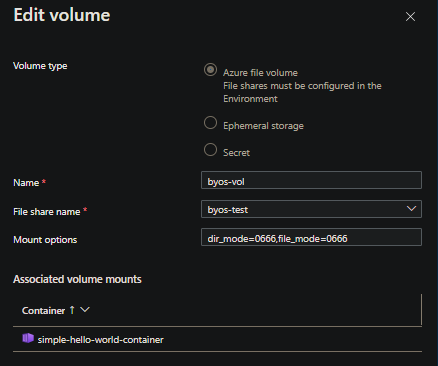
Prior to passing in something like dir_mode=0666,file_mode=0666 and assuming our SMB mount is at /data/tmp, mount permissions would look like the following:
sh-5.1# ls -lrtah /data
total 8.0K
drwxrwxrwx 2 root root 0 Aug 30 13:15 tmp
Afterwards, you can see the change reflected - this change would also be recursive and affect the contents of the file share:
sh-5.1# ls -lrtah /data
total 8.0K
drw-rw-rw- 2 root root 0 Aug 30 13:15 tmp
NFS
NFS volumes can be created by following Container Apps - Azure Files volume - NFS
NFS shares allow users to change directory/file permissions at runtime - for example, from within the shell of a container, or at application startup/runtime, as opposed to SMB/CIFS, where you need to instead use Mount options. NFS shares do not require Mount options to change these permissions.
By default, an NFS resource is mounted as 777. You can use something like chmod to change directory permissions. Below is prior to changing permissions of an NFS share mounted to the container:
sh-5.1# ls -lrtah /data
total 8.5K
drwxrwxrwx 2 root root 64 Dec 27 19:40 nfs
drwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4.0K Dec 27 19:40 ..
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4.0K Dec 27 19:40 .
Below is after:
sh-5.1# chmod 666 /data/nfs
sh-5.1# ls -lrtah /data
total 8.5K
drw-rw-rw- 2 root root 64 Dec 27 19:40 nfs
drwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4.0K Dec 27 19:40 ..
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4.0K Dec 27 19:40 .
These changes in permissions will persist independently of the Container App lifecycle. For example, if one app changes the permissions of the NFS volume from 777 to 666, and another app mounts it - the new Container App will have the NFS volume mounted with the most recently changed permissions which was set to 666.