Enabling e2e TLS with Azure Container Apps
This post will cover how to enable end-to-end TLS on Azure Container Apps.
Overview
On Azure Container Apps, Ingress and more specifically the proxy to the application, uses Envoy. By default, Envoy is set up to handle TLS termination/offloading. Which means that from Envoy -> your application will be proxied as an HTTP request. From the point of the Load Balancer to Envoy, is where HTTPS/TLS is handled.
Starting in more recent API versions, it is possible to enable full e2e TLS functionality. However, please be aware this is not publicly documented and thus subject to change - do this change at your own risk.
Enabling e2e TLS
There are two main points to making this work.
- 1) Enabling the configuration setting that turns this “on”
- 2) Instrumenting your application to listen for HTTPS requests. Which means enabling TLS on whatever server is running your application in your codebase
Ingress configuration
To enable this, you need to set targetPortHttpScheme to true. By default, this is null. In the portal on recent API versions, you can navigate to your Azure Container App -> Overview -> select JSON Overview, then you should be able to see this property.
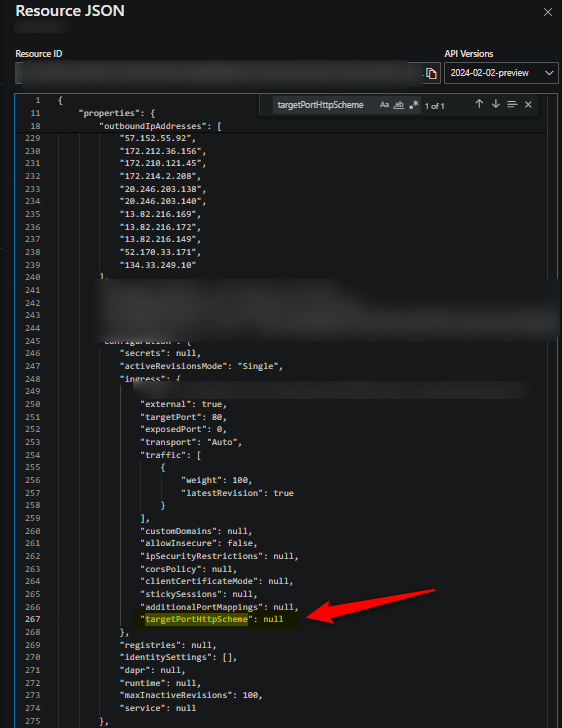
As of writing this post, this cannot be done through the portal, but can be done through the Azure CLI (and potentially through other IaC methods). Run the following:
-
az containerapp show -g some-rg -n someapp -o yaml > app.yamlThis will write out the Container Apps metadata into a
.yamlfile. Next, updatetargetPortHttpSchemein that file to the following:targetPortHttpScheme: https -
Update the Container App with the change in your
.yamlfile withaz containerapp update -n someapp -g some-rg --yaml app.yaml
You may need to restart the revision (or create a new revision) after this change for it to take effect.
Application
Most web servers by default will listen over a HTTP (non-TLS) port. Common implementations today require developers to opt-in to use a TLS enabled server. This part will vary based on framework/language.
This should be tested in a local environment first, after enabling TLS on the applications server in your codebase. The example uses Go with Fiber:
(main.go)
package main
import (
"github.com/gofiber/fiber/v2"
"go.uber.org/zap"
controllers "container-apps-e2e-tls-go/controllers"
)
func init() {
zap.ReplaceGlobals(zap.Must(zap.NewProduction()))
}
func main() {
app := fiber.New()
app.Get("/", controllers.IndexController)
zap.L().Info("Go Fiber starting HTTPS server on port 3443")
err := app.ListenTLS(":3443", "./certs/example.com.crt", "./certs/example.com.key")
if err != nil {
zap.L().Error("Failed to start server", zap.Error(err))
}
}
The relevant line here is app.ListenTLS. Consult your language/frameworks documentation as needed.
In this example, it is entirely possible to just use a self-signed certificate on the server. This will suffice for proxied HTTPS requests from Envoy on Azure Container Apps, as well. The certificate you want to use for your TLS server is ultimately up to you.
If you want to use a self-signed certificate, you can create one easily with the following command:
openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:4096 -sha256 -nodes -keyout example.com.key -out example.com.crt
Change the command as needed.
After this portion is done, browse to https://localhost:[your_app_port]. If you can access the application locally over https://, then at this point this can be redeployed to Container Apps for e2e TLS functionality.
“This combination of host and port requires TLS”
If you see responses like:
This combination of host and port requires TLS(or ones similiar to this)- Or,
retried and the latest reset reason: connection termination
Then you will need to ensure both main steps above are followed. If both were not enabled, as in, configuring targetPortHttpScheme: https on the Container App - and - enabling your appliction to use a TLS server via code, then these errors may appear.
In all other scenarios, especially for general upstream connect error or disconnect/reset before headers errors, review application logs by following Application Logging in Azure Container Apps