Avoiding hardcoding Node versions on App Service Windows
This post shows a few ways to avoid hardcoding Node.js versions with Windows App Services. This will focus on two files, web.config and iisnode.yml where this would most likely have a hardcoded Node version, as well as the required App Setting of WEBSITE_NODE_DEFAULT_VERSION.
With PaaS services, such as App Services, the platform underneath is managed for you - therefor over time versions(major, minor, or patch) may be upgraded, removed, or deprecated. Given this, it is best to not hardcode to a specific version within code as this may cause unintended issues down the road.
In the Azure Portal
When creating a Node.js application, the Node version is reliant upon the value set in WEBSITE_NODE_DEFAULT_VERSION, which is an App Setting created by default. This is only relevant on Windows and Node.js App Services.
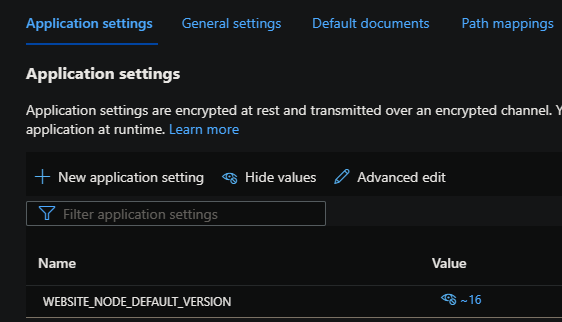
The tilda syntax (~) is equivalent of targetting the latest minor of that major available at the current time on the Instances the application is running on.
Since this is set to ~16, this would target the latest minor available of Node v16. If this minor is removed or a new latest minor version is available, this will target the next available minor of Node v16 available on that machine.
This is the recommended method and can help avoid the scenarios encountered as described earlier. This should be done regardless of the web.config and/or iisnode.yml configuration.
NOTE: This assumes you are not additionally hardcoding a version within web.config or iisnode.yml
You can read further about this here.
Web.Config
NOTE: Ensure that
WEBSITES_NODE_DEFAULT_VERSIONis set appropriately as mentioned here if you will be attempting the below methods.
The below example is using a typical web.config with a Node application.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!--
This configuration file is required if iisnode is used to run node processes behind
IIS or IIS Express. For more information, visit:
https://github.com/tjanczuk/iisnode/blob/master/src/samples/configuration/web.config
-->
<configuration>
<system.webServer>
<!-- Visit http://blogs.msdn.com/b/windowsazure/archive/2013/11/14/introduction-to-websockets-on-windows-azure-web-sites.aspx for more information on WebSocket support -->
<webSocket enabled="false" />
<handlers>
<!-- Indicates that the server.js file is a node.js site to be handled by the iisnode module -->
<add name="iisnode" path="server.js" verb="*" modules="iisnode"/>
</handlers>
<rewrite>
<rules>
<!-- Do not interfere with requests for node-inspector debugging -->
<rule name="NodeInspector" patternSyntax="ECMAScript" stopProcessing="true">
<match url="^server.js\/debug[\/]?" />
</rule>
<!-- First we consider whether the incoming URL matches a physical file in the /public folder -->
<rule name="StaticContent">
<action type="Rewrite" url="public{REQUEST_URI}"/>
</rule>
<!-- All other URLs are mapped to the node.js site entry point -->
<rule name="DynamicContent">
<conditions>
<add input="{REQUEST_FILENAME}" matchType="IsFile" negate="True"/>
</conditions>
<action type="Rewrite" url="server.js"/>
</rule>
</rules>
</rewrite>
<!-- 'bin' directory has no special meaning in node.js and apps can be placed in it -->
<security>
<requestFiltering>
<hiddenSegments>
<remove segment="bin"/>
</hiddenSegments>
</requestFiltering>
</security>
<!-- Make sure error responses are left untouched -->
<httpErrors existingResponse="PassThrough" />
<!--
You can control how Node is hosted within IIS using the following options:
* watchedFiles: semi-colon separated list of files that will be watched for changes to restart the server
* node_env: will be propagated to node as NODE_ENV environment variable
* debuggingEnabled - controls whether the built-in debugger is enabled
See https://github.com/tjanczuk/iisnode/blob/master/src/samples/configuration/web.config for a full list of options
-->
<!--<iisnode watchedFiles="web.config;*.js"/>-->
</system.webServer>
</configuration>
The below <iisnode nodeProcessCommandLine=".." /> can be added to the above web.config.
Not recommended:
<iisnode nodeProcessCommandLine="D:\Program Files (x86)\nodejs\16.13.0\node.exe"/>
Although this may work, this has the potential of breaking the application if either major, minor or patch is removed. This will throw a HTTP 500.1002, but can show other ranges of HTTP 500.1xxx status codes.
Details on IISNode status and sub status codes can be found here.
Recommended
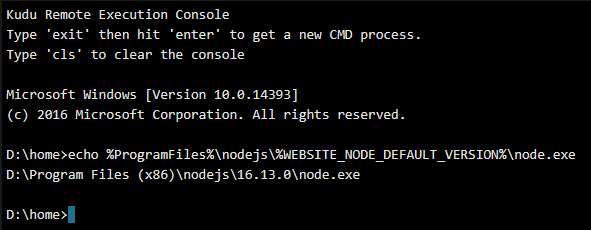
<iisnode nodeProcessCommandLine="%ProgramFiles%\nodejs\%WEBSITE_NODE_DEFAULT_VERSION%\node.exe"/>
We can see that if we echo out %ProgramFiles%\nodejs\%WEBSITE_NODE_DEFAULT_VERSION%\node.exe this resolves to the proper path. This ensures that if the version changes, it will still be pointing to a valid Node version.
iisnode.yml
NOTE: Ensure that
WEBSITES_NODE_DEFAULT_VERSIONis set appropriately as mentioned here if you will be attempting the below methods.
You can change iisnode through iisnode.yml which overrides any iisnode configuration in web.config. Since this also provides nodeProcessCommandLine, this leaves us open to the same possibility above.
Not recommended:
nodeProcessCommandLine: D:\Program Files (x86)\nodejs\16.13.0\node.exe
This is hardcoding to a specific path and can cause the same problems mentioned in the Web.Config section.
Recommended:
Instead you can avoid passing any path and instead do something like nodeProcessCommandLine: node. As long as WEBSITES_NODE_DEFAULT_VERSION is set, it will be able to take the proper node.exe from path.
If absolutely needing to have a full path in nodeProcessCommandLine, you can specify environment variables, like this example: nodeProcessCommandLine: "%ProgramFiles%\\nodejs\\%WEBSITE_NODE_DEFAULT_VERSION%\\node.exe"
Troubleshooting
The iisnode module is unable to start the node.exe process. Make sure the node.exe executable is available at the location specified
Resolution:
Ensure that the targetted path for node with the web.config is pointing to a valid and existing path. Additionally ensure there is no syntax errors which may cause the path to be interpreted as invalid.
The iisnode module is unable to start the node.exe process. Make sure the node.exe executable is available at the location specified in the system.webServer/iisnode/@nodeProcessCommandLine element of web.config. By default node.exe is expected in one of the directories listed in the PATH environment variable.
Resolution:
This is also due to either the node.exe not being found due to an incorrect path or due to syntax issues. Although the message presents itself as being due to web.config, this can happen if nodeProcessCommandLine is defined in iisnode.yml, which may appear misleading.
HTTP 500.1xxx’s after changes
Syntax issues or invalid paths can surface as HTTP 500.1002’s or other 1000-range substatus codes after changing web.config and/or iisnode.yml.
Review this link here on IISNode status codes as well as your web.config and iisnode.yml, if it exists.