Installing troubleshooting tools in a Container Apps ‘hello-world’ image
This post will cover installing networking troubleshooting tools into the Container Apps ‘hello-world’ quickstart image
Overview
Currently, the ‘hello-world’ quickstart image used when creating a new Container App via the Azure Portal and enabling the “Quickstart” image option does not container typical troubleshooting tools.
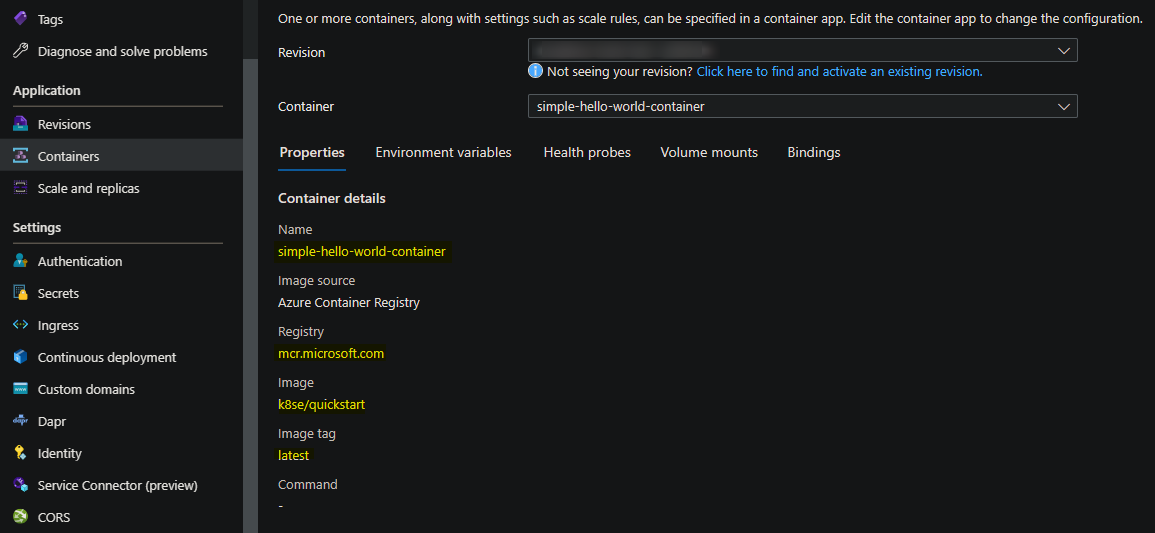
The image used is mcr.microsoft.com/k8se/quickstart:latest. This can be pulled locally and tested with, regarding the package installation below, as well.
This image uses CBL-mariner 2.x - which subsequentially uses the tdnf package manager. yum and rpm is available as a package manager as well.
CBL-mariner’s package manager is based off of dnf which is based off of yum - and also has RPM repository usage. There is commonality here given that RHEL/Fedora or others use this as well.
For more information on CBL-mariner’s package managers and other general information, see here.
If needed, update the package repository with tdnf update -yy prior to installation of below packages.
Installing tools like these in a “test” container can be useful in scenarios where you’re trying to troubleshoot network connectivity issues between hosts - and/or if the “main” application is currently not accessible or down.
Troubleshooting tools
nc
To install nc (netcat), run the following:
tdnf install nc -yy
You can check the version to ensure it’s installed
sh-5.1# nc -v
Ncat: Version 7.93 ( https://nmap.org/ncat )
Ncat: You must specify a host to connect to. QUITTING.
nslookup and dig
To install nslookup and dig, you need the bind-utils package:
tdnf install bind-utils -yy
nslookup and dig should now be installed:
sh-5.1# nslookup google.com
Server: 127.0.0.11
Address: 127.0.0.11#53
Non-authoritative answer:
Name: google.com
Address: 172.253.63.100
....
sh-5.1# dig -v
DiG 9.16.44
netstat
You can install netstat by installing net-tools:
tdnf install net-tools -yy
Check the version to ensure it’s now installed:
sh-5.1# netstat --version
net-tools 2.10
Fred Baumgarten, Alan Cox, Bernd Eckenfels, Phil Blundell, Tuan Hoang, Brian Micek and others
+NEW_ADDRT +RTF_IRTT +RTF_REJECT +FW_MASQUERADE -I18N
AF: (inet) +UNIX +INET +INET6 +IPX +AX25 +NETROM +X25 +ATALK -ECONET +ROSE -BLUETOOTH
HW: +ETHER +ARC +SLIP +PPP +TUNNEL -TR +AX25 +NETROM +X25 +FR +ROSE +ASH +SIT +FDDI +HIPPI +HDLC/LAPB +EUI64
wget
To install wget, install the wget package:
tdnf install wget -yy
Validate this is now installed:
sh-5.1# wget --version
GNU Wget 1.21.2 built on linux-gnu.
traceroute
To install traceroute, use the traceroute package:
tdnf install traceroute -yy
Check the version for installation confirmation:
sh-5.1# traceroute --version
Modern traceroute for Linux, version 2.1.3
Copyright (c) 2016 Dmitry Butskoy, License: GPL v2 or any later
tcptraceroute
You can install tcptraceroute with the following packages:
tdnf install traceroute util-linux
NOTE: Without
util-linuxyou’ll get/usr/bin/tcptraceroute: line 29: getopt: command not foundwhen trying to invoke thetcptraceroutecommand
tcpping
tcpping has a few prerequisites for proper usage.
- Install
bcwithtdnf install bc -yy - Install the
awkcommand -tdnf install gawk -yy - Install the
traceroutepackage. See the tcptraceroute section - Install the
wgetpackage. See the wget section
Install tcpping with the following:
cd /usr/bin
wget http://www.vdberg.org/~richard/tcpping
chmod 755 tcpping
Confirm this is now installed:
sh-5.1# tcpping google.com
traceroute to google.com (172.253.122.101), 255 hops max, 52 byte packets
seq 0: tcp response from bh-in-f101.1e100.net (172.253.122.101) <syn,ack> 2.850 ms
traceroute to google.com (142.251.167.139), 255 hops max, 52 byte packets
seq 1: tcp response from ww-in-f139.1e100.net (142.251.167.139) <syn,ack> 2.165 ms
tcpdump
tcpdump can be installed with the following:
tdnf install -y tcpdump
You can confirm installation by checking the version:
sh-5.1# tcpdump --version
tcpdump version 4.99.1
libpcap version 1.10.1 (with TPACKET_V3)
OpenSSL 1.1.1k FIPS 25 Mar 2021
ssh
You can install an openssh client in replacement of telnet (which ideally shouldn’t be used over other better tools nowadays) with the following:
tdnf install openssh-clients
Validate that the command can now be used:
sh-5.1# ssh
usage: ssh [-46AaCfGgKkMNnqsTtVvXxYy] [-B bind_interface]
[-b bind_address] [-c cipher_spec] [-D [bind_address:]port]
[-E log_file] [-e escape_char] [-F configfile] [-I pkcs11]
[-i identity_file] [-J [user@]host[:port]] [-L address]
[-l login_name] [-m mac_spec] [-O ctl_cmd] [-o option] [-p port]
[-Q query_option] [-R address] [-S ctl_path] [-W host:port]
[-w local_tun[:remote_tun]] destination [command [argument ...]]