Installing database clients to connect and troubleshoot database connections
This post will show how to install various database client tools to connect to databases from SSH on App Service Linux, Web Apps for Containers, or Containers Apps
Overview
This post can technically apply to most environments where a container is ran and where you have access to open a shell into the container.
Sometimes, you may encounter an issue where an application is having issues connecting to a database, or, certain queries when done through application code do not generate the result you expected, amongst other potential issues.
Through the SSH option on the App Service Linux Kudu site, you can connect to your container and use the below approach. For “Blessed Images”, SSH is already enabled.
For custom images, you may need to enable SSH - if so, review Enabling SSH on Linux Web App for Containers. If SSH is not able to enabled into a custom image, then what’s covered in this blog post may not be able to be done for creating a connection from that particular application.
For Container Apps, you don’t need to install an SSH server into your image - but you do need access to the Console - which effectively opens a shell to your container.
NOTE: On App Service Linux, do not try to install these packages through the “Bash” option - Bash opens a shell in the Kudu container where you’re running as
kudu_ssh_user(non-root) - therefor package installation will fail. This must be done in the application container (“SSH” option).
Test connectivity
First, it may be good to test general connectivity and name resolution.
Name resolution:
You can use the nslookup command. Run nslookup [yourdatabasehost]. If this is an Azure Database for MySQL server, run nslookup somemysqlserver.mysql.database.azure.com, for example - or with Azure SQL, use somesqlserver.database.windows.net. Replace the host name with the relavant FQDN of the database server.
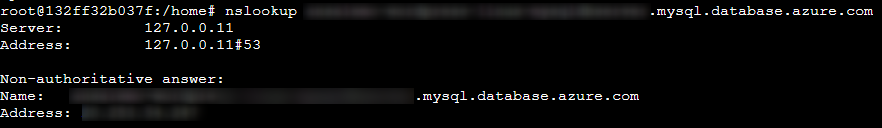
If this is not installed in the container, run the following:
- Ubuntu/Debian:
apt-get install dnsutils - Alpine:
apk add bind-tools - Mariner:
tdnf install bind-utils - RHEL/CentOS:
yum install bind-utils
If name resolution fails then subsequent commands and steps below will not work, this will need to be focused on first.
Connections:
We can test if the database server is able to establish a connection from us, the client, by using the nc (netcat) command.
If this is not installed in the container, run the following:
- Ubuntu/Debian:
apt-get install netcat- Note: If you see
E: Package 'netcat' has no installation candidateuseapt-get install netcat-traditionalinstead
- Note: If you see
- Alpine:
apk add netcat-openbsd - Mariner:
tdnf install nc - RHEL/CentOS:
yum install nc
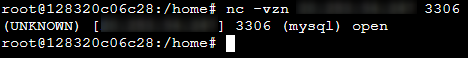
This example is ran within a Debian-based container. We’re running the nc command nc -vzn [mysql_ip] [mysql_port] which confirms that a connection to port 3306 for our MySQL server can be established - remember to target the correct port of your database (eg., SQL is typically 1433, Redis may be 6379 or 6380, etc.). If this fails, review if traffic is allowed to the destination (eg., firewall on the server, UDR/RTs, Virtual Appliances, etc.). You should see something like the below.
Database clients
MySQL and MariaDB
This was covered in Using MySQL clients to connect to a MySQL database from App Service Linux. Follow this for a walkthrough.
SQL
sqlcmd may not be installed in most images using mssql, as this is apart of the mssql-tools optional-based packages.
In an SSH session within the application container on App Service Linux - or through the Console option on Container Apps, install the mssql-tools18 package depending on the distribution used from the container image. If you’re not sure of the distro, run cat /etc/os-release.
Ubuntu/Debian
Run the following within an SSH session:
apt-get update
ACCEPT_EULA=Y apt-get install mssql-tools18
You can also follow along with what’s here - although be sure to not use sudo
Alpine:
You can effectively follow what’s here. Below is a slightly simplified version:
# Download the desired package(s)
curl -O https://download.microsoft.com/download/3/5/5/355d7943-a338-41a7-858d-53b259ea33f5/msodbcsql18_18.3.3.1-1_amd64.apk
curl -O https://download.microsoft.com/download/3/5/5/355d7943-a338-41a7-858d-53b259ea33f5/mssql-tools18_18.3.1.1-1_amd64.apk
# (Optional) Verify signature, if 'gpg' is missing install it using 'apk add gnupg':
curl -O https://download.microsoft.com/download/3/5/5/355d7943-a338-41a7-858d-53b259ea33f5/msodbcsql18_18.3.3.1-1_amd64.sig
curl -O https://download.microsoft.com/download/3/5/5/355d7943-a338-41a7-858d-53b259ea33f5/mssql-tools18_18.3.1.1-1_amd64.sig
curl https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc | gpg --import -
gpg --verify msodbcsql18_18.3.3.1-1_amd64.sig msodbcsql18_18.3.3.1-1_amd64.apk
gpg --verify mssql-tools18_18.3.1.1-1_amd64.sig mssql-tools18_18.3.1.1-1_amd64.apk
# Install the package(s)
apk add --allow-untrusted msodbcsql18_18.3.3.1-1_amd64.apk
apk add --allow-untrusted mssql-tools18_18.3.1.1-1_amd64.apk
NOTE: This removes
sudo, since it can’t be used, and sets$architecturefrom the above link toamd64
RHEL/CentOS
You can follow what’s in Install SQL-Server command line tools on Linux for the most part. Although remove any usage of sudo. Below are simplified commands:
- Use this if using RHEL 9
curl https://packages.microsoft.com/config/rhel/9/prod.repo | tee /etc/yum.repos.d/mssql-release.repo - Use this if using RHEL 8
curl https://packages.microsoft.com/config/rhel/8/prod.repo | tee /etc/yum.repos.d/mssql-release.repo - Use this if using RHEL 7
curl https://packages.microsoft.com/config/rhel/7/prod.repo | sudo tee /etc/yum.repos.d/mssql-release.repo - Install the tools:
yum install -y mssql-tools18 unixODBC-devel
Mariner
Run the following:
tdnf update
tdnf install mssql-tools18
Note, you may encounter Sqlcmd: Error: Microsoft ODBC Driver 18 for SQL Server : SSL Provider: [error:1416F086:SSL routines:tls_process_server_certificate:certificate verify failed:unable to get issuer certificate]
If so, pass the -C flag to your command - eg., sqlcmd -S yourserver.database.windows.net -U [username] -P [password] -d [database] -C
Usage
Next, add mssql-tools to $PATH. Overwise you need to invoke it from /opt/mssql-tools18/bin/sqlcmd
- Run:
export PATH="$PATH:/opt/mssql-tools18/bin"
You can now connect to the SQL server with:
sqlcmd -S [sqlserver].database.windows.net -U [username] -P [password]- If you want to connect to a specific database, pass the
-dflag -
If you want to execute a query through
sqlcmd- pass the-qflag:sqlcmd -S [sqlserver].database.windows.net -U [username] -P [password] -d default -Q "SELECT * FROM todos". You’d see something like this:root@303dca088506:/# sqlcmd -S some-sql.database.windows.net -U user -P password -d default -Q "SELECT * FROM todos" Id todo completed ----------- --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- --------- 1 sweep the floor 0 2 clean the car 0 3 mow the grass 1 4 vacuum the carpet 1 (4 rows affected)
- If you want to connect to a specific database, pass the
NOTE: If you want to install tools for version 17, use
mssql-tools17
Redis
Ubuntu/Debian
To install Redis, run:
apt-get update
apt-get install redis-tools
You can alternatively install just the redis package, redis-server, or redis-cli. However, the Redis client versions maybe different depending on which package is used.
Alpine
Run the following:
apk add redis
RHEL/CentOS
Run the following:
dnf install redisoryum install redis
Mariner
- Given that the
redispackage with Mariner does not install a newer client, therefor not providing the--tlsoption, you can opt to install from source. Use the following:
tdnf update
tdnf install build-essential \
wget \
tar \
which \
openssl-devel
wget --no-check-certificate https://download.redis.io/redis-stable.tar.gz
tar -xzvf redis-stable.tar.gz
cd redis-stable
make BUILD_TLS=yes
make install
NOTE: If you get
fatal error: jemalloc/jemalloc.h: No such file or directory, runmake distclean
Installing from source will take a while to complete.
After a succesful compilation, redis-cli will be put on $PATH
- Or,
tdnf install redis- Note, this installs the 6.x client - if you need to connect over TLS, install a more recent version. If you do not need to connect over TLS (port 6380), then this option is probably fine
Usage
Note, depending on the redis-cli client version (eg., 6.x vs. 7.x) - the --tls option may not be enabled and you may see:
Unrecognized option or bad number of args for: '--tls'
You can run redis-cli -v to ensure that --tls is a part of your CLI version. If needed, you can manually download. If you happen to be compiling from source, run make BUILD_TLS=yes
If you recieve SSL_Connect failed: certificate verify failed - pass the --insecure option to ignore certificate checking.
Connect with TLS:
redis-cli -h mycache.redis.cache.windows.net -a "access_key=" -p 6380 --tls
Connect without TLS:
redis-cli -h mycache.redis.cache.windows.net -a "access_key=" -p 6379
The 6.x version clients should suffice for installation if TLS is not required
You can then run a query within Redis after connecting:
myredis.redis.cache.windows.net:6380> KEYS *
1) "ddeeff"
2) "aabbcc"
Postgres
Ubuntu/Debian
You can install psql with:
apt-get update
apt-get install postgresql
Alpine
Run the following:
apk add postgresql
RHEL/CentOS
If postgresql packages are not available, first run dnf install https://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/reporpms/EL-8-x86_64/pgdg-redhat-repo-latest.noarch.rpm
- Then run:
dnf install postgresql[version_number] - eg.,
dnf install postgresql16
Mariner
To install postgresql, run the following:
tdnf install postgresql
Usage
Usage would be through the psql command. Below is an example command, where -d is passed to connect to an existing database in the remote Postgresql server. Otherwise psql tries to connect to a database that is named after the username provided.
psql -h mydatabase.postgres.database.azure.com -U myuser -p 5432 -d somedatabase