Setting up a basic Elasticsearch container on Container Apps
This post will cover deploying and setting up a basic Elasticsearch container on Azure Container Apps
Overview
Elasticsearch is a search and analytics software that’s widely known and popular - which also makes up part of the ELK stack. This post will cover deploying a basic Elasticsearch image from Dockerhub and running it on Azure Container Apps
Deployment
This example will use the portal. You can use IaC or the AZ CLI, amongst other potential options, to create the application.
-
Navigate to the “Create a resource” option and search for “Container Apps” in the market place. Fill out the required fields:
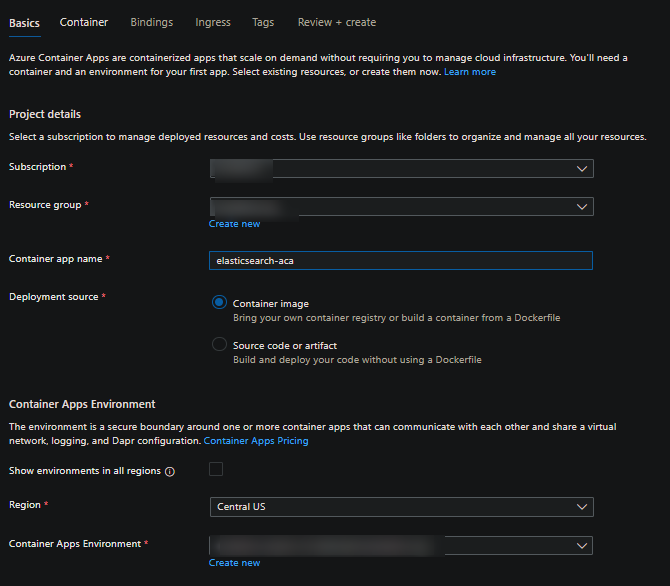
- Fill our the required fields under the Container blade. Set the following notable fields:
- Image source: Docker hub or other registrieis
- Image type: Public
- Registry login server: docker.io
- Image and tag: elasticsearch:8.15.0
For Workload profile (not available on Consumption-only SKU), CPU cores, Memory, etc. - fill these out are deemed fit
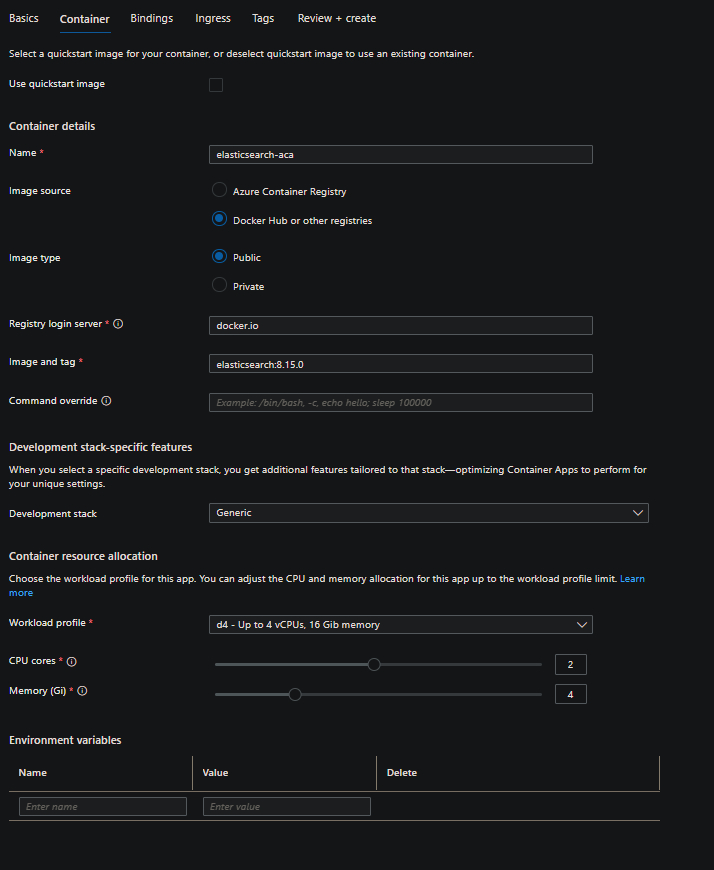
IMPORTANT: This examples uses the 8.15.0 tag - which has a notable change from 7.x which will be explained later. You can use a 7.x tag version if desired
-
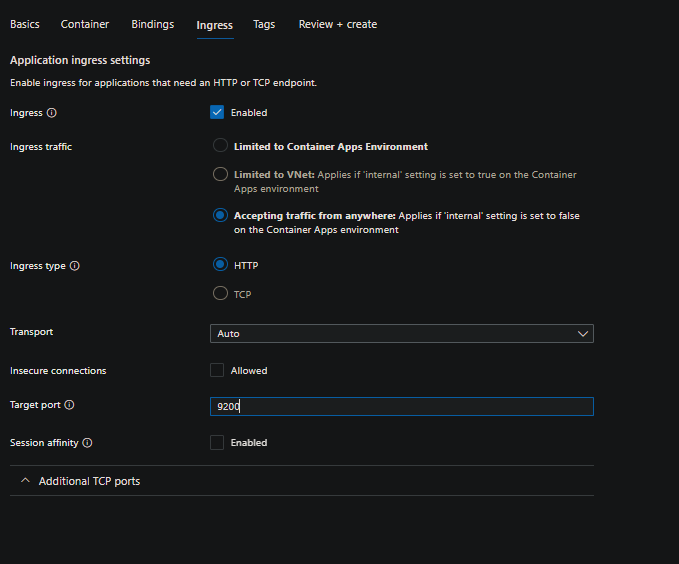
Set up your ingress. In this example, we’ll be using external ingress. Make sure to set the port to 9200 regardless of your ingress type.
-
Click Review + create to create the Container App
- As seen in the Container blade, you have the options to set environment variables through here. We’ll need to add some to get the application functional. But for the sake of explanation of what needs to be configured, we’ll talk about this in the next section.
Configuration
Environment variables
You’ll need to set two environment variables here to get this to work. This comes with some caveats. The biggest is needing to run in single-node. If this is a blocker for certain projects, it would be best to run on a platform (such as an Azure Linux VM or AKS) where you have host access to change vm.max_map_count - as without setting discovery.typeto single-node will have Elasticsearch’s logic go through Bootstrap Checks that will cause the container to fail to start, typically with the error regarding vm.max_map_count being too low due to underlying nodes mmap configuration.
IMPORTANT: PaaS services like Container Apps, Spring Apps, Web App for Containers, etc. all do not let users set
vm.max_map_count
discovery.type=single-node. What this does is explained here. When setting this, this will surpress the error at startup ofMax virtual memory areas vm.max_map_count [65530] is too low, increase to at least [262144]- which cannot be set on Container Apps since this will avoid certain bootstrap checks. .xpack.security.enabled=false. Starting with 8.x - HTTPS is enabled by default for these Elasticsearch images. On Container Apps, the proxied request between Envoy and the pod is through HTTP - as TLS offloading happens at the Load Balancer, which is infront of Envoy. This should be set, or else you’ll get HTTP 502’s (even thoug the container is running in the pod) or potentialreceived plaintext http traffic on an https channelwarnings.- If using a 7.x image - you may not need to set this.
To add an environment variable - go to Containers -> select the container to Edit -> Environment Variables and then click “Save”
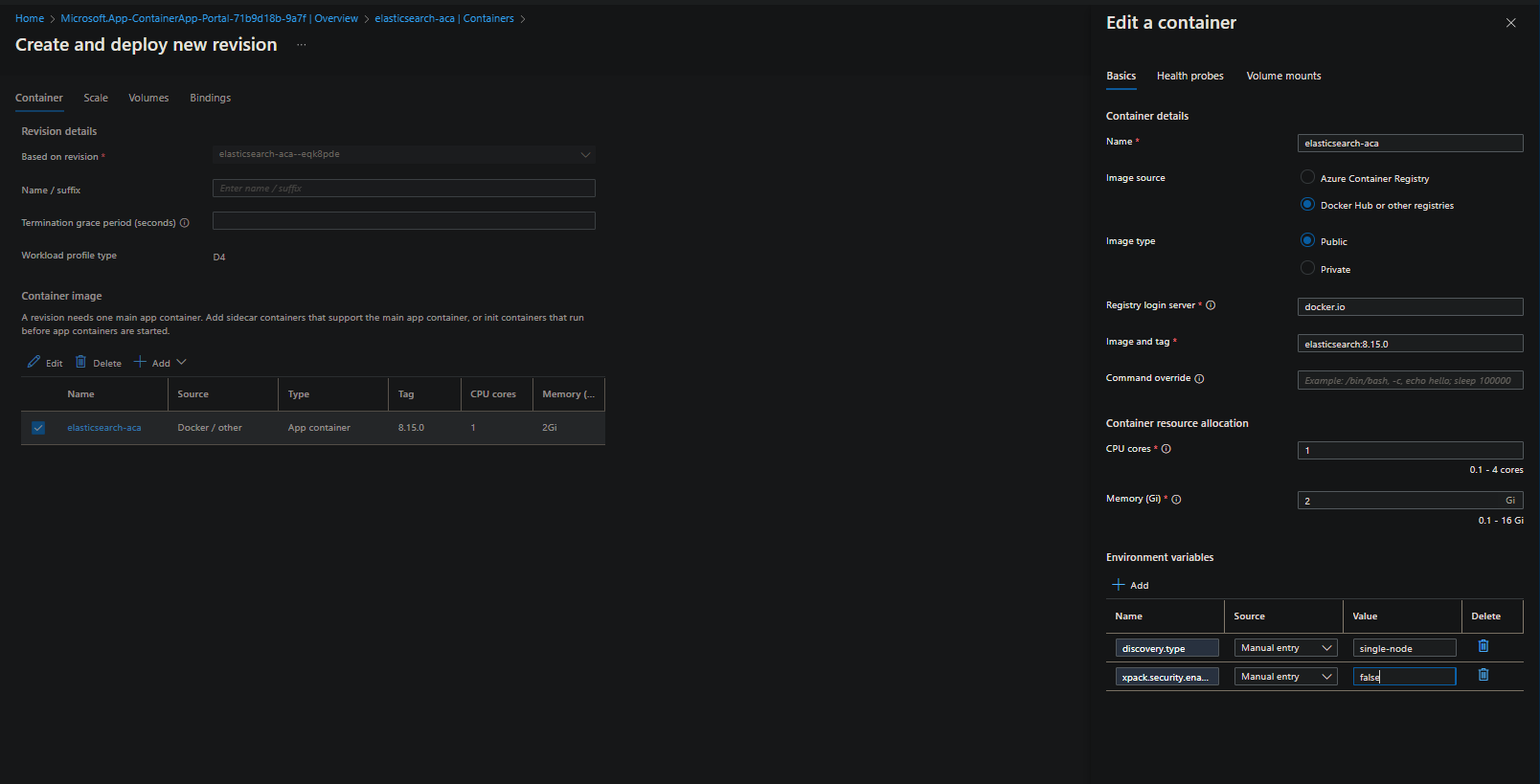
Volumes
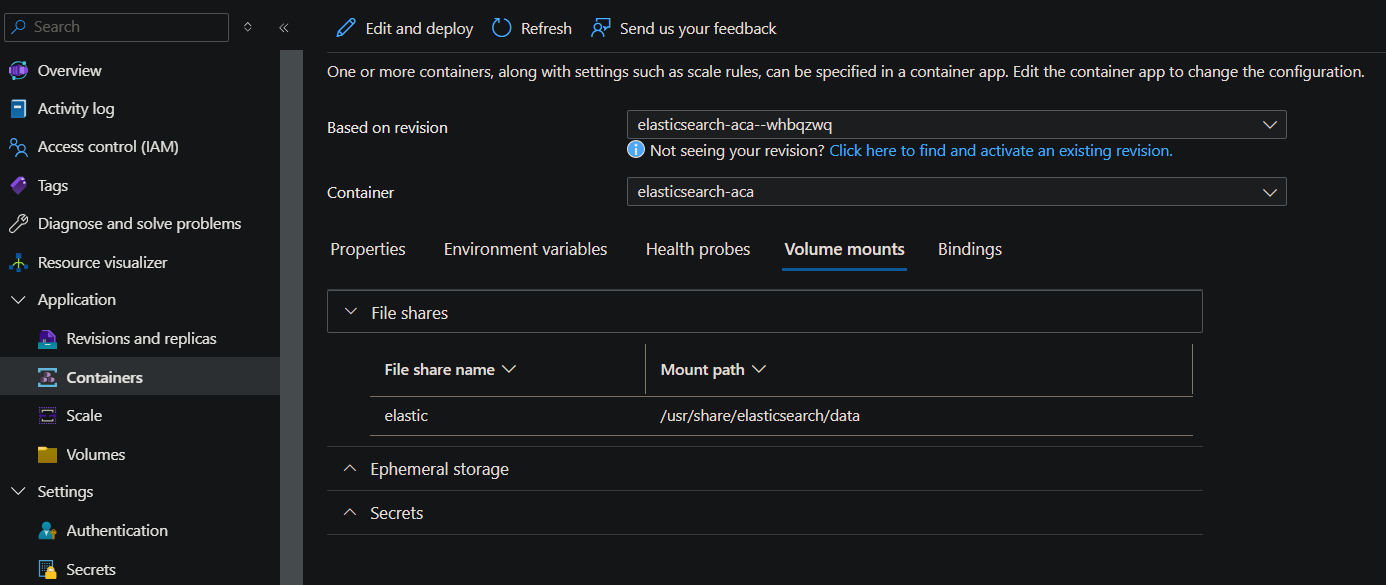
We need to persist the search data, to do so, we can use Azure Files and mount it as a persistent volume. Otherwise, given that containers (and pods) are ephemeral, data will be lost after a new pod is created or a container is restarted.
Add a Storage resource on the Container App Environment and then add a volume to the container mapped to the /usr/share/elasticsearch/data directory.
Follow Use storage mounts in Azure Container Apps on how to configure volumes for a container.
Usage
After configuring the above, we should be able to test the application.
- Add an index:
curl -X PUT https://elasticsearch.funnyname-12345-abc.someregion.azurecontainerapps.io/cities- In logging (
ContainerAppConsoleLogs_CL/ContainerAppConsoleLogs/ Logstream, etc.) you should see this message:[cities] creating index, cause [api], templates [], shards [1]/[1]
- In logging (
- Add data:
curl -X POST -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{ "city": "rome", "country": "it" }' https://elasticsearch.funnyname-12345-abc.someregion.azurecontainerapps.io/cities/_doccurl -X POST -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{ "city": "tokyo", "country": "jp" }' https://elasticsearch.funnyname-12345-abc.someregion.azurecontainerapps.io/cities/_doccurl -X POST -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{ "city": "paris", "fr": "it" }' https://elasticsearch.funnyname-12345-abc.someregion.azurecontainerapps.io/cities/_doc
-
Query the data - you can use various clients:
curl -X GET "https://elasticsearch.funnyname-12345-abc.someregion.azurecontainerapps.io/cities/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json'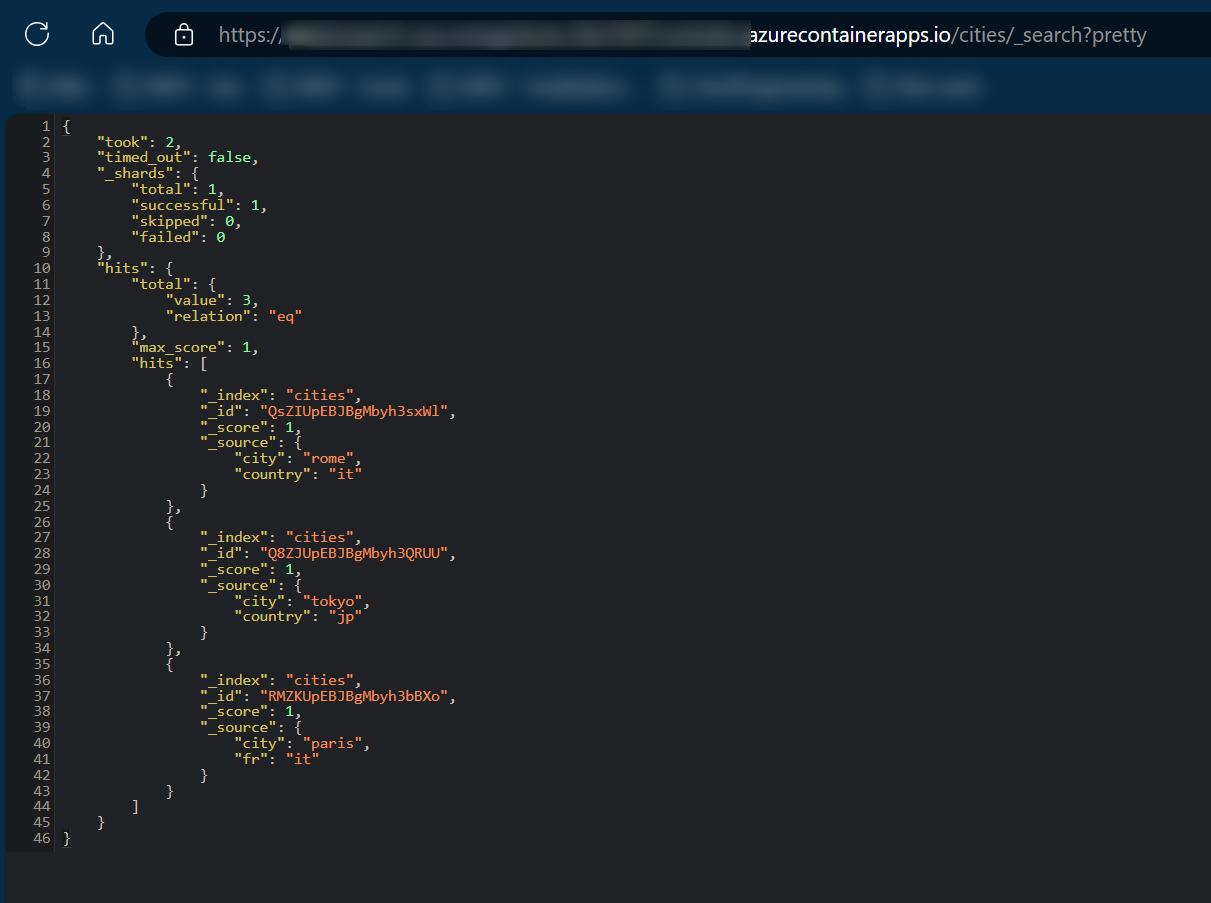
Troubleshooting
max virtual memory areas vm.max_map_count [65530] is too low, increase to at least [262144]
This will surface if not running discovery.type of single-node. The common way to resolve this is to have some type of host access to change vm.max_map_count - however as explained earlier this cannot be done on Container Apps (and other services)
received plaintext http traffic on an https channel
This will occur if you’re using an Elasticversion of 8.x or higher since TLS is enabled by default. Set xpack.security.enabled = false to overcome this.
java.lang.IllegalStateException: failed to obtain node locks
The full message in this context is java.lang.IllegalStateException: failed to obtain node locks, tried [/usr/share/elasticsearch/data]; maybe these locations are not writable or multiple nodes were started on the same data path?.
This will occur if the nobrl mount option is not set. This is to allow file writes when Container Apps are going through pod activity. See Preventing File Locks when mounting storage on Azure Container Apps
Issues with restarts
There may be certain behavior where Elasticsearch acts in the following when a restart (ex. a new pod is creating while the other one is being removed, thus an overlap situation occurs briefly (see the ‘restarted’ blog post above))
java.io.IOError: java.nio.file.NoSuchFileException: /usr/share/elasticsearch/data/some/file- This may end up recovering on its own
- This doesn’t recover and requires
_stateto be deleted
This behavior may not be ideal - coupled with the single-node usage, if this behavior is encountered, it may be best to run the Elasticsearch image on other services that are not PaaS, in general, like IaaS, where host access can be done by end-users to change Elasticsearch where this won’t be a restriction, given much of Elasticsearch’s documentation points to this type of unrestricted configuration.