Deploying WAR based Java applications with CI/CD (Azure DevOps) on App Service Windows
In this blog post we’ll cover some examples of how to deploy war based applications to Windows App Service using Azure DevOps.
Overview
This section will cover CI/CD deployment for war-based applications - this is for Blessed Tomcat images, which will act as our Web Container for our war. With this image, you still have the option to choose your Java major version, as well as Apache Tomcat major and minor version - but the premise is that we’re deploying a war file into a Tomcat container, which Tomcat itself will run.
Below is a configuration reference from the portal:
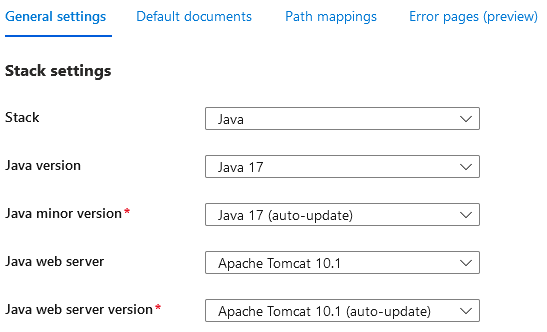
This is not the same as running a Java SE “Blessed” Image which requires this to be an executable war with an embedded Web Server.
This post will also include deployment differences for Maven and Gradle.
Local Development
Configuring for Maven
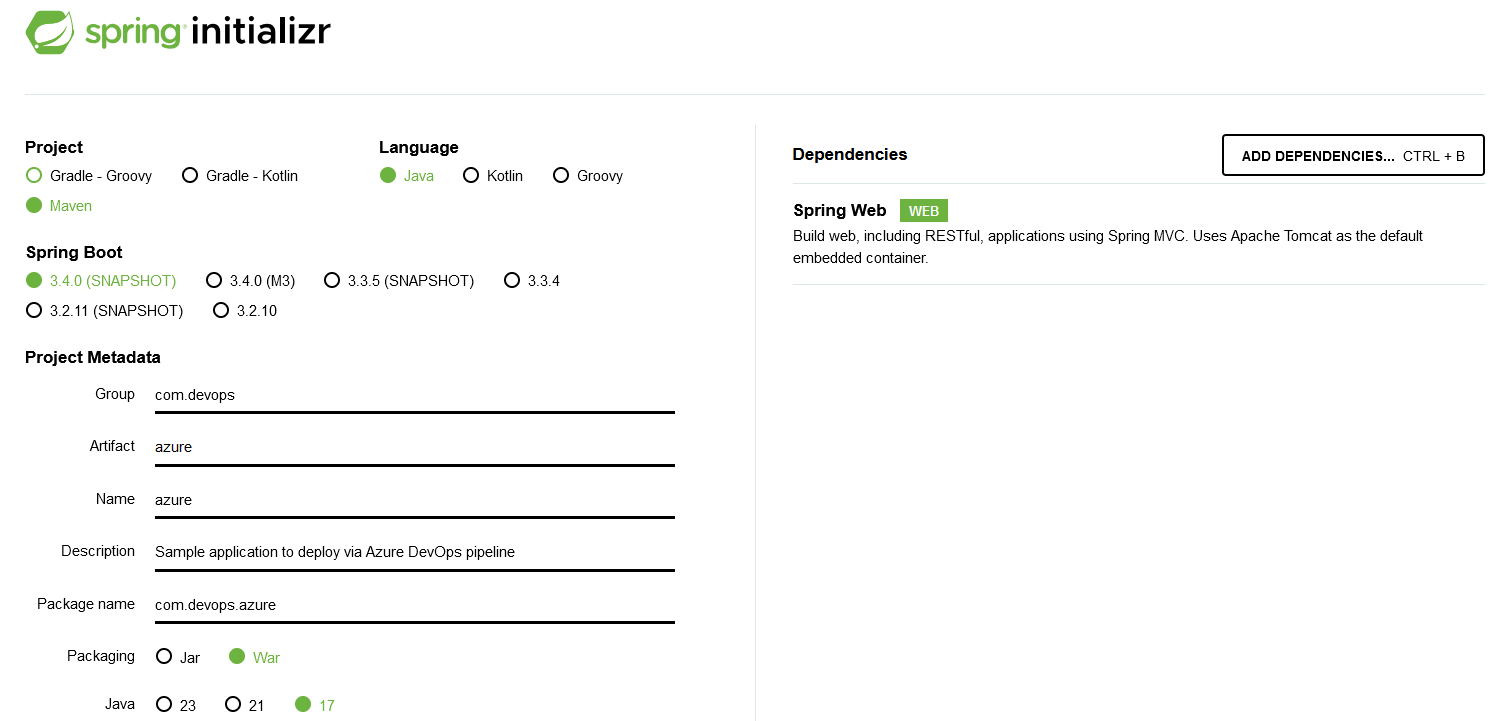
- Go to Spring Initializr and create the application with the following properties:
- Project: Maven
- Language: Java
- Spring Boot: 3.4.0 (SNAPSHOT)
- Project Metadata: Fill this as fits your needs
- Packaging: War
- Java: 17
For Dependencies, go to Add Dependencies and choose Spring Web. Click Generate after this, which will download a zip which we’ll extract into a project workspace.
- After downloading the zip, extract it on your local machine and cd into the folder with the source code.
- In a terminal, run either of the following:
- If Maven is on $PATH, run
mvn spring-boot:runrelative to thepom.xml. - If Maven is not on $PATH, run
./mvnw spring-boot:runrelative to thepom.xml
- If Maven is on $PATH, run
NOTE: This assumes you have Java 17 locally. Maven needs to point to a Java 17 installation as well. If you’re unsure to what Maven is using, use
mvn -v.
After running the above command, you should see some output like the below in your terminal:
2024-11-03T21:01:16.889-06:00 INFO 28988 --- [azure] [ main] o.apache.catalina.core.StandardService : Starting service [Tomcat]
2024-11-03T21:01:16.889-06:00 INFO 28988 --- [azure] [ main] o.apache.catalina.core.StandardEngine : Starting Servlet engine: [Apache Tomcat/10.1.31]
2024-11-03T21:01:16.966-06:00 INFO 28988 --- [azure] [ main] o.a.c.c.C.[Tomcat].[localhost].[/] : Initializing Spring embedded WebApplicationContext
2024-11-03T21:01:16.967-06:00 INFO 28988 --- [azure] [ main] w.s.c.ServletWebServerApplicationContext : Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in 1007 ms
2024-11-03T21:01:17.328-06:00 INFO 28988 --- [azure] [ main] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat started on port 8080 (http) with context path '/'
2024-11-03T21:01:17.346-06:00 INFO 28988 --- [azure] [ main] com.devops.azure.AzureApplication : Started AzureApplication in 1.936 seconds (process running for 2.302)
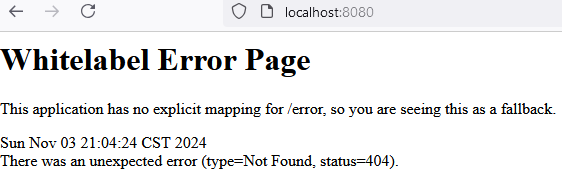
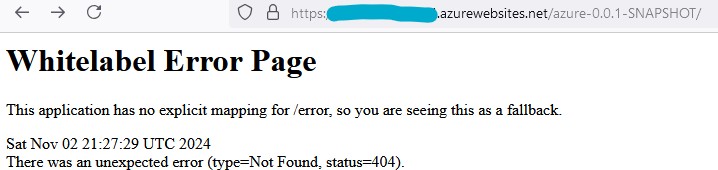
- Browsing to localhost:8080 should show a Whitelabel Error Page, which is expected, since we have no Controllers serving our root path.
- Let’s add a Controller and model to show at the REST URL when hitting /greeting. Under your project src, relative to your entrypoint
.javafile, create a controller and a model. Let’s name is GreetingController.java and Greeting.java. The project structure should look like this:
| - src
| | - main
| | - java
| | - com
| | - devops
| | - azure
| | GreetingController.java
| | Greeting.java
- Add the following code to GreetingController.java
package com.devops.azure;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class GreetingController {
private static final String template = "Hello, %s!";
private final AtomicLong counter = new AtomicLong();
@GetMapping("/greeting")
public Greeting greeting(@RequestParam(value = "name", defaultValue = "World") String name) {
return new Greeting(counter.incrementAndGet(), String.format(template, name));
}
}
- Add the following code to Greeting.java
package com.devops.azure;
public record Greeting(long id, String content) { }
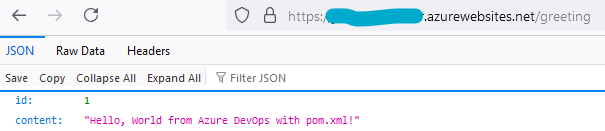
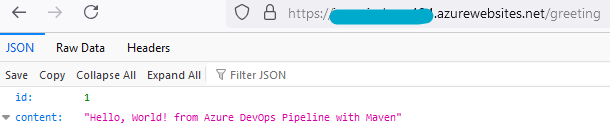
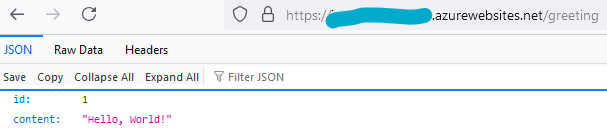
- Restart the application. Refresh the browser, we should now see the below output at /greeting:
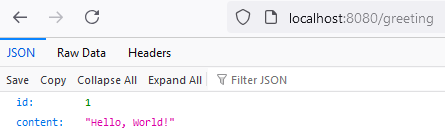
- Push this code to a repository of your choosing to use later on for the DevOps section.
Configuring for Gradle
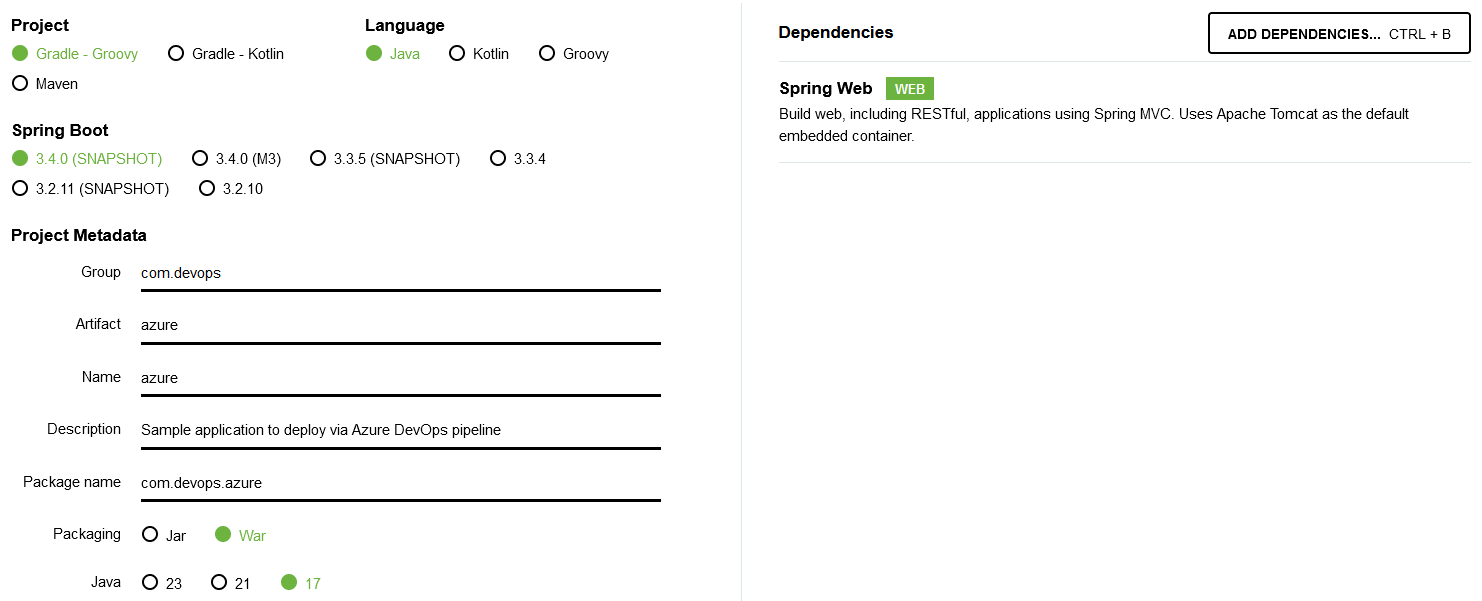
- Go to Spring Initializr and create the application with the following properties:
- Project: Gradle - Groovy / Gradle - Kotlin (I selected Gradle - Groovy)
- Language: Java
- Spring Boot: 3.4.0 (SNAPSHOT)
- Project Metadata: Fill this as fits your needs
- Packaging: War
- Java: 17
For Dependencies, go to Add Dependencies and choose Spring Web. Click Generate after this, which will download a zip which we’ll extract into a project workspace.
- After downloading the zip, extract it on your local machine and cd into the folder with the source code.
- In a terminal, run ./gradlew bootRun to start the Spring Boot application. You should see the same output above as discussed in th Maven section.
DevOps
Prerequisites:
- If not done so already, create an Azure DevOps Organization.
- Next, create a Azure DevOps Project to host our pipeline after this.
Creating the pipeline:
In your Azure DevOps project go to:
- Create azure-pipleines.yml
- Pipelines -> Pipelines -> New Pipeline -> Azure DevOps
- Select the repository that is hosting the code
- Select the classification (Production / Non-production) -> assign a service -> Configure Pipeline
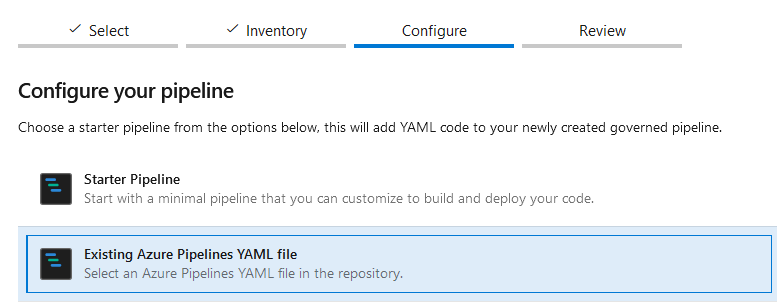
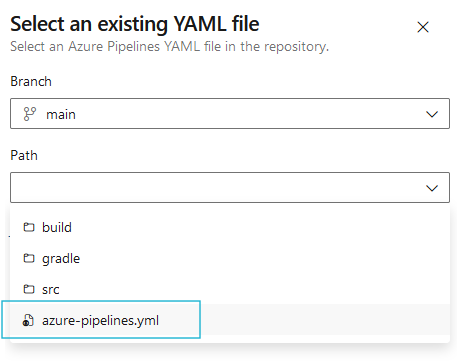
- Select the Existing Azure Pipelines YAML file and browse azure-pipelines.yml (use the templates provided in the following Maven / Gradle sections) from your project:
Maven
# Maven package Java project Web App to Windows on Azure
# Build your Java project and deploy it to Azure as a Windows web app
# Add steps that analyze code, save build artifacts, deploy, and more:
# https://docs.microsoft.com/azure/devops/pipelines/languages/java
trigger:
- main
variables:
# Azure Resource Manager connection created during pipeline creation
azureSubscription: 'sc deploy to app service'
# Web app name
webAppName: 'myapp'
# Environment name
environmentName: 'myapp'
# Agent VM image name
vmImageName: 'ubuntu-latest'
stages:
- stage: Build
displayName: Build stage
jobs:
- job: MavenPackageAndPublishArtifacts
displayName: Maven Package and Publish Artifacts
pool:
vmImage: $(vmImageName)
steps:
- task: Maven@3
displayName: 'Maven Package'
inputs:
mavenPomFile: 'pom.xml'
# We add jdkVersionOption to point to Java 17 for Maven
jdkVersionOption: 1.17
- task: CopyFiles@2
displayName: 'Copy Files to artifact staging directory'
inputs:
SourceFolder: '$(System.DefaultWorkingDirectory)'
Contents: '**/target/*.?(war|jar)'
TargetFolder: $(Build.ArtifactStagingDirectory)
- upload: $(Build.ArtifactStagingDirectory)
artifact: drop
- stage: Deploy
displayName: Deploy stage
dependsOn: Build
condition: succeeded()
jobs:
- deployment: DeployWindowsWebApp
displayName: Deploy Windows Web App
environment: $(environmentName)
pool:
vmImage: $(vmImageName)
strategy:
runOnce:
deploy:
steps:
- task: AzureWebApp@1
displayName: 'Azure Web App Deploy: myapp'
inputs:
azureSubscription: $(azureSubscription)
appType: webApp
appName: $(webAppName)
package: '$(Pipeline.Workspace)/drop/**/target/*.?(war|jar)'
# IMPORTANT: If you don't add this it will deploy to a context named after your WAR
# ex. yoursite.azurewebsites.net/azure-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT/
customDeployFolder: 'ROOT'
Note Make sure to Authorize the pipeline for deployment. Click into the pipeline to view and permit this. This should be a one time operation.
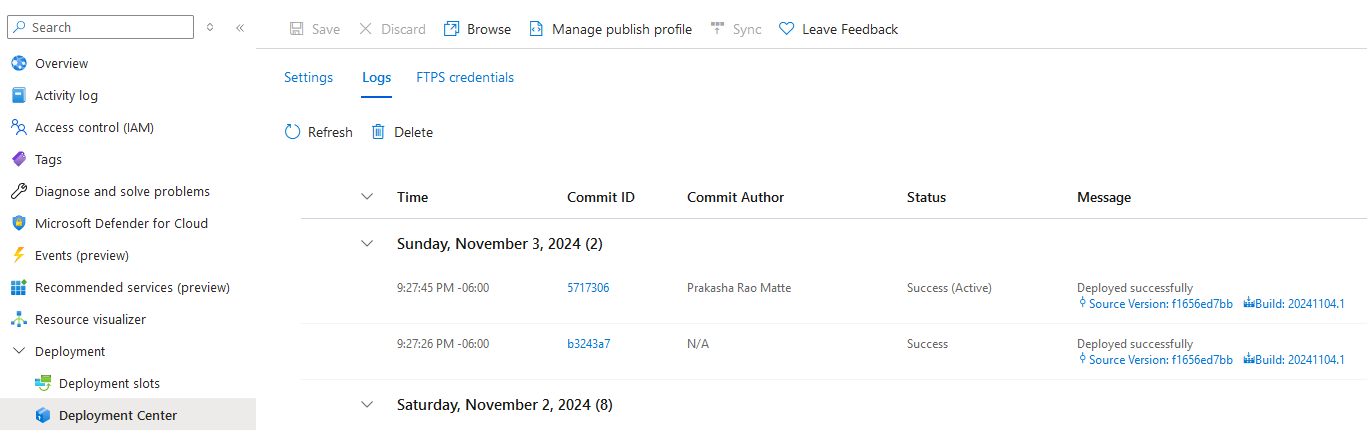
Once the build was succesful from Azure DevOps pipeline, you could validate the deployment at the following two places from App Service.
- Go to portal.azure.com -> App Service -> Deployment Center
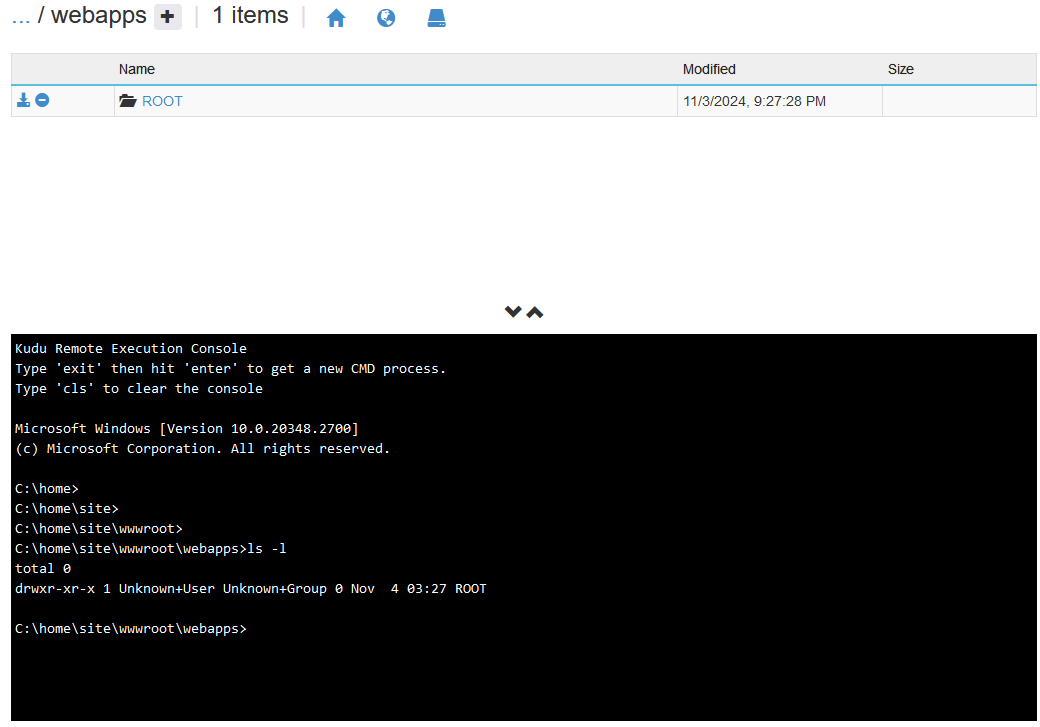
- Go to portal.azure.com -> App Service -> Advanced Tools -> Debug Console -> CMD
- At this point after deployment, we should be able to browse our application on Azure.
You can view the Maven task documentation for further configuration here.
Azure DevOps - Why am I getting a 404 after deployment?
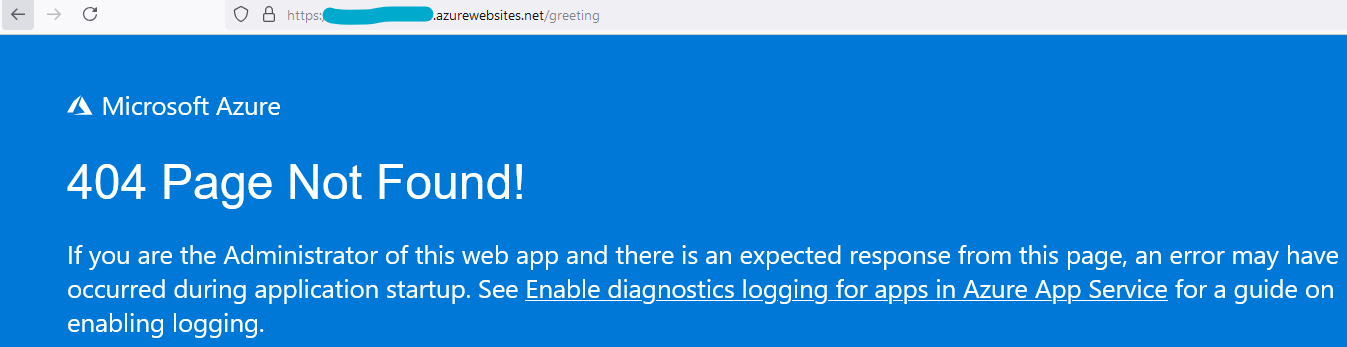
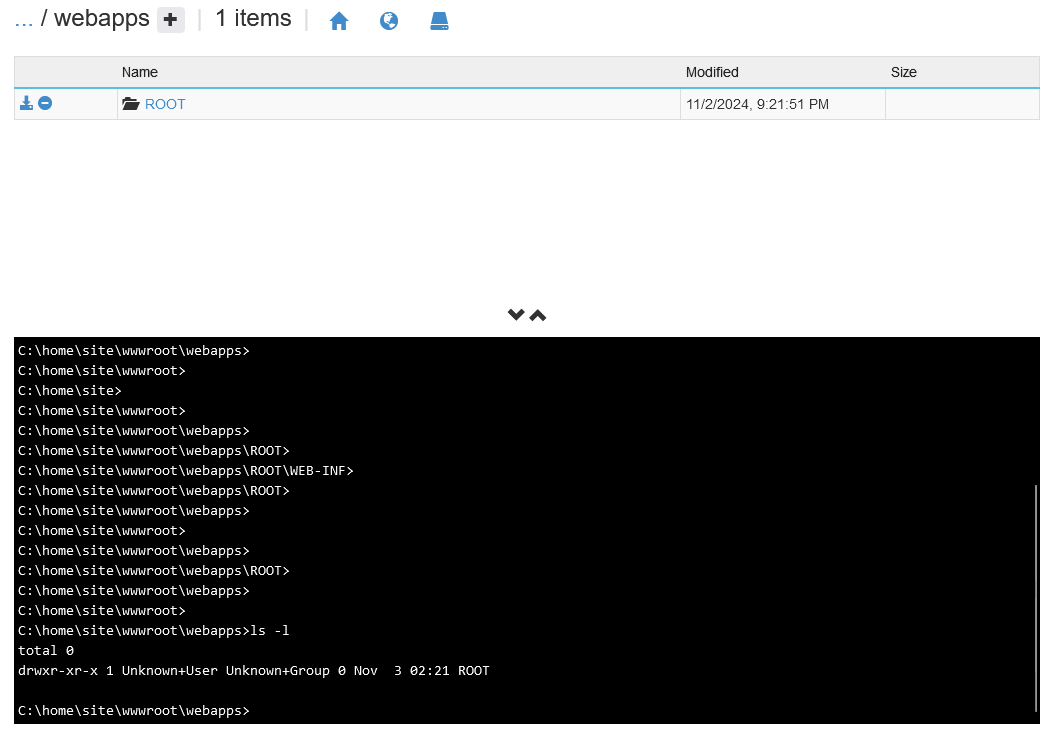
If you’re following along with the above, you should be able to get a pipeline quickly spun up with a succesful deployment. However, if you are expecting your site content to show up on the site’s root path (“/”) but did not add the customDeployFolder property (seen above), you may see this 404 after deployment:
You’ll see that when this deployment API is used it creates a webapps folder under wwwroot containing our exploded war:
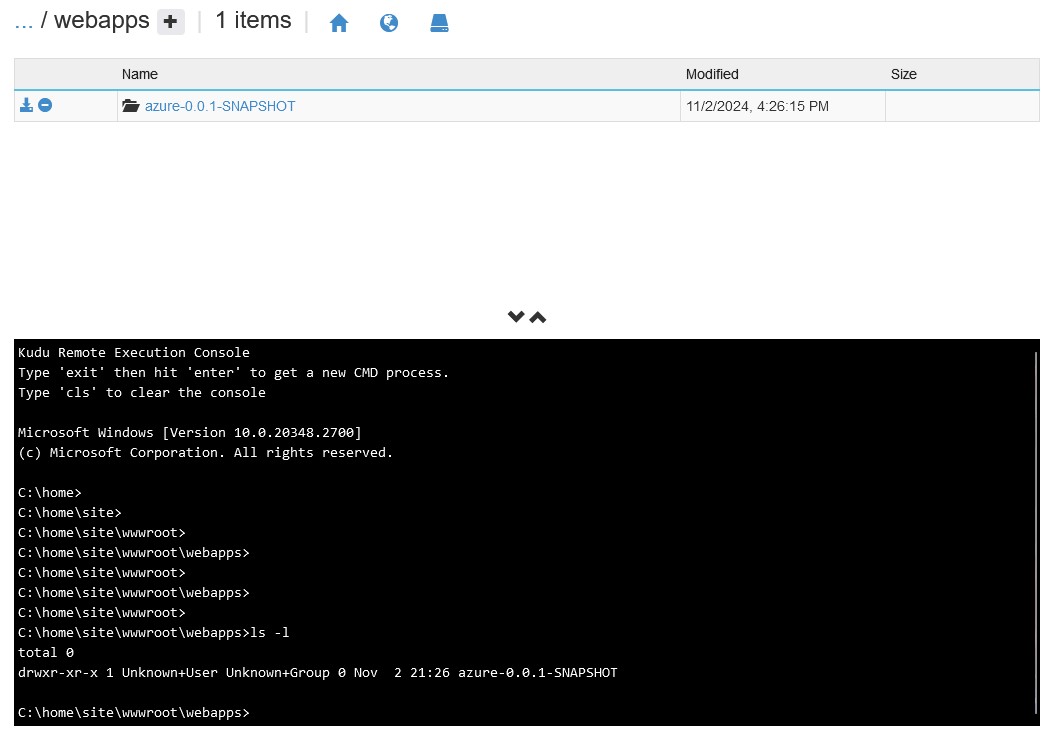
This is because, by default, the API’s used in this deployment task pass the name of our war to the name parameter in the War Deploy URI being called. Therefore, if your war isn’t named ROOT, it will always deploy to a different context named after your war file.
This is opposed to the OneDeploy API being used on deployment methods such as the Azure CLI or the Maven Plugin which, under the hood, rename our war (or jar) to app.war and deploy directly to wwwroot instead of wwwroot/webapps. This in turn is mapped directly to the root context (“/”).
Another quick way to solve this, aside from using the customDeployFolder property is to add the <finalName></finalName> element to the <build></build> section of your pom.xml. Such as:
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
<finalName>ROOT</finalName>
</build>
This will package the war with the name defined here and is what will be passed to the name parameter described above.
Gradle
# Maven package Java project Web App to Windows on Azure
# Build your Java project and deploy it to Azure as a Windows web app
# Add steps that analyze code, save build artifacts, deploy, and more:
# https://docs.microsoft.com/azure/devops/pipelines/languages/java
trigger:
- main
variables:
# Azure Resource Manager connection created during pipeline creation
azureSubscription: 'sc deploy to app service'
# Web app name
webAppName: 'myapp'
# Environment name
environmentName: 'myapp'
# Agent VM image name
vmImageName: 'ubuntu-latest'
stages:
- stage: Build
displayName: Build stage
jobs:
- job: GradlePackageAndPublishArtifacts
displayName: Gradle Package and Publish Artifacts
pool:
vmImage: $(vmImageName)
steps:
# We add this to set Java 17 for our pipeline environment
- task: JavaToolInstaller@0
inputs:
versionSpec: '17'
jdkArchitectureOption: 'x64'
jdkSourceOption: 'PreInstalled'
# We add this Gradle task to build with Gradle
- task: Gradle@3
inputs:
gradleWrapperFile: 'gradlew'
tasks: 'build'
javaHomeOption: 'JDKVersion'
- task: CopyFiles@2
displayName: 'Copy Files to artifact staging directory'
inputs:
SourceFolder: '$(System.DefaultWorkingDirectory)'
Contents: '**/build/libs/your_war.war'
TargetFolder: $(Build.ArtifactStagingDirectory)
- upload: $(Build.ArtifactStagingDirectory)
artifact: drop
- stage: Deploy
displayName: Deploy stage
dependsOn: Build
condition: succeeded()
jobs:
- deployment: DeployWindowsWebApp
displayName: Deploy Windows Web App
environment: $(environmentName)
pool:
vmImage: $(vmImageName)
strategy:
runOnce:
deploy:
steps:
- task: AzureWebApp@1
displayName: 'Azure Web App Deploy: yourapp'
inputs:
azureSubscription: $(azureSubscription)
appType: webApp
appName: $(webAppName)
package: '$(Pipeline.Workspace)/drop/**/build/libs/your_war.war'
# IMPORTANT: If you don't add this it will deploy to a context named after your WAR
# ex. yoursite.azurewebsites.net/azure-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT/
customDeployFolder: 'ROOT'
Azure DevOps - Why am I getting a 404 after deployment?
The same applies to what was covered in the Maven section above.
Troubleshooting
App works on Embedded Server, but not on Tomcat Web Server in Azure
It is worth checking if it works fine in a local machine using the following steps.
- Download Apache Tomcat from https://tomcat.apache.org/download-10.cgi . Here I am using 10.1.31, but other versions are available in the same place.
- I downloaded and installed “32-bit/64-bit Windows Service Installer”
- If there is any conflict with the port while running the Tomcat, edit /conf/server.xml and change the port at the following place in server.xml
<Connector port="9000" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
connectionTimeout="20000"
redirectPort="8443"
maxParameterCount="1000"
/>
NOTE: I changed to 9000 as my other app runs at 8080, if you don’t have any other apps running at 8080 / tomcat default port, you don’t need to make any changes.
- Browse http://localhost:9000/manager/html
- If this prompots with Username and Password, grab tomcat user credentials from /conf/tomcat-users.xml. It will be in the
<tomcat-users></tomcat-users>section. - If you don’t find such thing, add the following line before </tomcat-users>
<user username="tomcat" password="xxyyzz" roles="manager-gui"/>
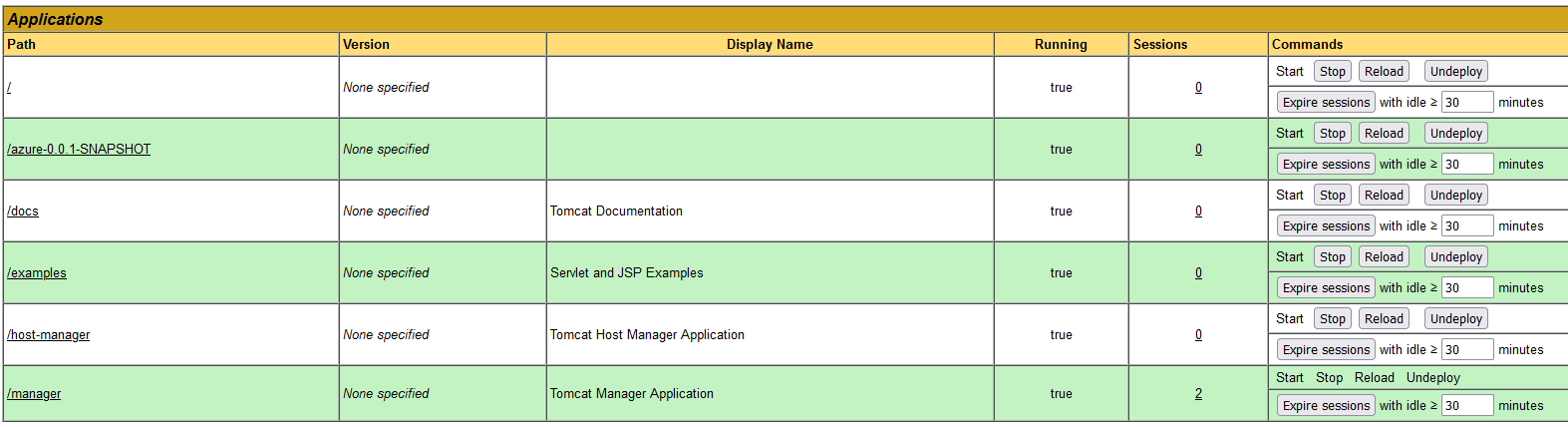
- Copy the generated war file in the /webapps folder. After sometime, the war file gets extracted and deployed in the Tomcat (as shown below), which you can access from the /manager.html in the browser.
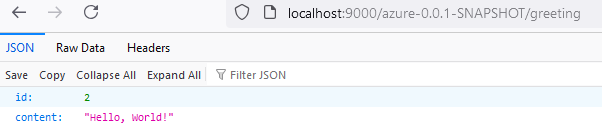
- When you access the extracted war folder, the app will load its content.
- If you see the same error as you saw in the Azure, fix it in the local machine and try deploying again.
NOTE: Sometimes, your app works in the IDE, but not in Web Server such as tomcat, that means there must be some configuration / code missing in the main class.