Increasing Request Header sizes on Linux App Services
Sometimes there is a need to increase the default request header size allowed when making HTTP requests to an application. For instance, there may be a large token in a request which can cause a HTTP 431 status code - Request Header Fields Too Large error. - if it exceeds the language’s your using default limit. Each language’s limit for allowed total header size varies by default.
On Linux App Services, various stacks can be hosted - below are some common ways to change a languges default request header size when using a Blessed Image.
NOTE: Depending on the application, a HTTP 400 may also be returned by the application when encountering this issue.
Code based examples can be found here.
Important information about request limits on App Service
The “Front Ends” that act as load balancers to the application(s) running behind them have a hard upper limit of 64KB for total request header sizes.
The Front End configuration is not able to be changed. This means that although the application side can be changed (as discussed below), and depending on the server running the application - may have a various default total header size limit, but in all cases, the upper limit will always only be 64KB in size.
Java
Tomcat
For Tomcat on Linux App Services, some custom configuration to the Tomcat installation will need to be done first. Follow this guide on how to change your CATALINA_BASE to move under /home/tomcat for persistence.
Once this is done, go to your /home/tomcat/conf/server.xml file and look for the Connector that contains the maxHttpHeaderSize property. Update this to a size that fits, the below example shows this increased to 30KB.
<Connector
port="${port.http}" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
maxThreads="${catalina.maxThreads}"
connectionTimeout="20000"
redirectPort="8443"
compression="on"
URIEncoding="UTF-8"
maxHttpHeaderSize="30000"
/>
The default value on Linux App Service has this set to about 16KB. The below was a test with sending a 27KB Request Header from Postman with the default ~16KB value set:
HTTP/1.1 400
Content-Length: 1980
Content-Type: text/html;charset=utf-8
Content-Language: en
Date: Fri, 03 Jun 2022 20:21:21 GMT
<!doctype html><html lang="en"><head><title>HTTP Status 400 – Bad Request</title><style type="text/css">body {font-family:Tahoma,Arial,sans-serif;} h1, h2, h3, b {color:white;background-color:#525D76;} h1 {font-size:22px;} h2 {font-size:16px;} h3 {font-size:14px;} p {font-size:12px;} a {color:black;} .line {height:1px;background-color:#525D76;border:none;}</style></head><body><h1>HTTP Status 400 – Bad Request</h1><hr class="line" /><p><b>Type</b> Exception Report</p><p><b>Message</b> Request header is too large</p>
Updating this to 30KB, as we did above, we can see this is now successful

Java SE
In something like Spring Boot, you may see the following if the overall header size is larger than what’s allowed, which is 8KB by default with Spring Boot:
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Request header is too large
Using Spring Boot as an example, we can increase the default values for request headers size. You can add an AppSetting named JAVA_OPTS to your App Service with the value of -Dserver.max-http-header-size=30000 which will pass this to the JVM.
Replace the 30000 (30KB) value of a value of your choice.

Node
In Node, you can increase header sizes with --max-http-header-size. If a request exceeds the allowed header side you may see an HTTP 431: 431 Request Header Fields Too Large.
In package.json, add the following to your scripts property where needed:
{
..other properties..
"scripts": {
"start": "node --max-http-header-size=30000 server.js"
},
"dependencies": {
...some dependencies..
}
}
Optionally, you can add an AppSetting with the name NODE_OPTIONS and a value of --max-http-header-size=30000

If you’re using PM2 to serve the node application, you can try the following options:
- Pass
node-argsto the PM2 start command:pm2 start server.js --node-args="--max-http-header-size=16000" - Or, use an
ecosystem.config.jsfile - below is an example:
module.exports = {
apps : [{
name: "app",
script: "./server.js",
node_args: "--max-http-header-size=16000"
env: {
NODE_ENV: "development",
},
env_production: {
NODE_ENV: "production",
}
}]
}
Single Page Applications (and other client-side JavaScript applications)
For applications using Angular, React, Vue and others - that fall into the SPA category - which is generally purely client-side executed code when served for production - you cannot directly increase header sizes without the help of serving this through some type of Web Server or process manage that allows arguments to change the header size.
This is because client-side executed code, on it’s own, which is code ran in the browser and not on the server - has no notion of how to set header sizes. Typically, there wouldn’t be any reason to increase header for client-side code only, unless the resource actually serving the content is needing this to be done.
Therefor some potential approaches to this could be the following:
- Run the production build assets from the SPA ontop of a Node HTTP server or framework
- Serve the production build through a Web Server like NGINX or Apache - the simplest way to do this on App Service is through a custom image
- If using something like PM2, you can try to add
--max-http-header-sizeinto the run arguments.
Python
Python and Linux App Services uses Gunicorn to help run wSGI based applications on Azure. Therefor configuring allowed request header sizes would be done on Gunicorn itself.
You may recieve a HTTP 400 Bad Request if headers are too large. You can increase this with the limit_request_field_size
In the Azure Portal go to your App Service and choose Configuration -> General Settings and then add gunicorn --bind 0.0.0.0:8000 --timeout 600 app:app --limit-request-field_size 64000 to the Startup Command field. This example sets allowed header sizes to 64KB. Change app:app to reflect your wSGI variable name and file name that contains the wSGI module.
This general approach using Gunicorn and passing –limit-request-field_size would work for most wSGI applications on Python and App Service Linux.
.NET Core
With .NET Core and Kestrel you can increase header sizes through the MaxRequestHeadersTotalSize property. This property has a default set to ~32KB for total header sizes.
If header size limits are hit, you’ll also encounter an HTTP 431 Request Header Fields Too Large error.
We can increase the allowed header size with something like the following with Kestrel:
builder.WebHost.UseKestrel(k =>
{
// Increase the Request limit size to 64KB
k.Limits.MaxRequestHeadersTotalSize = 64000;
});
PHP
PHP on Linux App Service uses Apache for PHP 7.4 Blessed Images and NGINX for PHP 8.x Blessed Images.
Apache
For Apache, we can increase the request header allowed values with the LimitRequestFieldSize directive. On Linux App Services, we’ll need to use a Custom Startup Script to do this.
- Go to the Kudu site for the application and select SSH.
- Run
cp /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/000-default.conf /hometo copy the configuration file over to home. Use an FTP client to download the file to your local machine or edit this file directly through the FTP client. Make sure our custom000-default.confconfiguration file is placed under/home/. - Edit the file to include the
LimitRequestFieldSizedirective set to the needed value. - Create a custom startup script and include the following:
#!/bin/bash
echo "Copying custom 000-default.conf over to /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/000-default.conf"
APACHE_CONF=/home/000-default.conf
if [ -f "$APACHE_CONF" ]; then
cp "$APACHE_CONF" /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/000-default.conf
else
echo "File does not exist, skipping cp."
fi
NOTE: We’re just copying directly over to sites-enabled since the 000-default.conf already exists there.
- Upload this startup script to the application using an FTP client. Place this under /home. This must be a Bash script (.sh file extension).
-
Go to the App Service and then choose Configuration -> General Settings and in the Startup command field enter
/home/startup.sh- Note, startup.sh is just an example name. Replace this with the Bash script name you uploaded.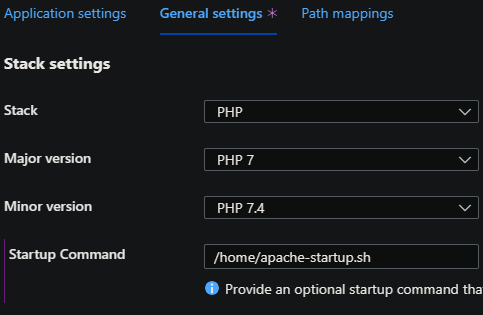
- Click save, which will restart the application, and the request header allowed values should now be updated.
NGINX
Increasing the allowed header size is mostly the same as the Apache method. NGINX’s directive that sets this value is client_header_buffer_size.
NGINX may throw back a a HTTP 400 Bad Request if headers are too large.
- Go to the Kudu site for the application and select SSH.
- Run
cp /etc/nginx/sites-available/default /hometo copy the configuration file over to home. Use an FTP client to download the file to your local machine or edit this file directly through the FTP client. Make sure our customdefaultconfiguration file is placed under/home/. - Edit the file to include the
client_header_buffer_sizedirective set to the needed value in yourserverblock. - Create a custom startup script and include the following:
#!/bin/bash
echo "Copying custom default.conf over to /etc/nginx/sites-available/default"
NGINX_CONF=/home/default.conf
if [ -f "$NGINX_CONF" ]; then
cp /home/default.conf /etc/nginx/sites-available/default
service nginx reload
else
echo "File does not exist, skipping cp."
fi
- Upload this startup script to the application using an FTP client. Place this under /home. This must be a Bash script (.sh file extension).
-
Go to the App Service and then choose Configuration -> General Settings and in the Startup command field enter
/home/startup.sh- Note, startup.sh is just an example name. Replace this with the Bash script name you uploaded.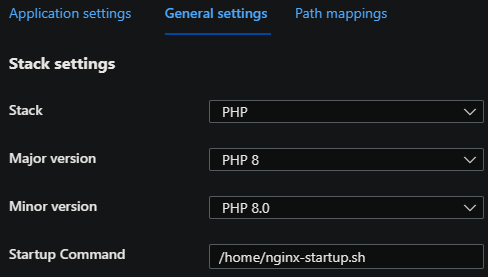
- Click save, which will restart the application, and the request header allowed values should now be updated.
Other services to note
If using other products such as Application Gateway or any services that act as a middleware (proxy), these services may have non-configurable Request Header Size limits.
If you are using services like this and still encountering this error after updating your application, like the above, try testing by removing or bypassing these services - which will normally sit infront of the application.